Password Reset
Forgot your password? Enter the email address you used to create your account to initiate a password reset.
Forgot your password? Enter the email address you used to create your account to initiate a password reset.
7 Minutes
by Michael G. Risbano, MD, MA, FCCP
The initial evaluation for patients referred with breathlessness or fatigue with exertion often utilizes resting diagnostic studies including echocardiography, pulmonary function tests, chest imaging, and blood work. While these tests may assist in diagnosing disease states, physiologic abnormalities and the prominence of a disease state in patients with multiple cardiopulmonary disorders often cannot be determined. Provocative testing with advanced cardiopulmonary exercise testing (ACPET) challenges the cardio-pulmonary-vascular and skeletal muscle systems to elicit a cascade of physiologic events not measurable at rest.1,2 The ACPET Program was instituted at UPMC Presbyterian Shadyside in June 2017, and since then, over 120 cases have been performed on patients with various cardiopulmonary disorders.
Advanced cardiopulmonary exercise testing includes breath-by-breath analysis of ventilatory gas exchange and invasive measurement of pulmonary vascular and cardiac function in association with upright cycle ergometer and electrocardiogram (ECG) exercise testing.3 ACPET provides full physiologic assessment of patients referred for exertional dyspnea and fatigue. With the ACPET modality, cardiac output, pulmonary artery pressures, multiple ventilatory indices, systemic pressures, and ECG variables are simultaneously assessed during a progressive intensity exercise provocation. Performing the study in the upright, seated position on a stationary bicycle ergometer replicates daily activities as almost all efforts are performed against gravity in the upright position (see Figure 1).
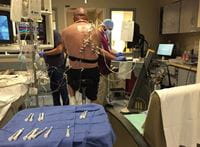
Figure 1: ACPET in action in the Cardiac Cath Lab at UPMC Presbyterian.
ACPET can delineate disease states related to pulmonary arterial, pulmonary venous, cardiac valvular, loading dynamics, autonomic, and skeletal muscle pathophysiologies that limit exercise capacity. Non-invasive CPET testing can be safely performed in patients with various disease states such as pulmonary arterial hypertension;4 however, without the invasive component, the pulmonary vascular pressures and resistances, as well as cardiac output, are unknown. With ACPET, there is direct measurement of cardiopulmonary vascular hemodynamics, which provides gold standard information about hemodynamic response to exercise in conjunction with ventilatory mechanics and breath-by-breath analysis.
ACPET at UPMC Presbyterian Shadyside involves the placement of a pulmonary artery catheter into the right internal jugular vein (see Figure 2) and a radial arterial line under ultrasound guidance in the cardiac catheterization lab. A resting supine pulmonary artery (PA) catheterization is performed to establish baseline values. The resting portion may include a shunt run or response to pulmonary vasodilators, if indicated. Once completed, the patient is seated in an upright position and cardiopulmonary hemodynamics are re-measured, as a change in body position often affects pressures, vascular resistance, and cardiac outputs. The patient is then connected to the CPET/metabolic cart, to obtain baseline resting values. Pulmonary gas exchange is measured with the Ultima™ CardiO2 gas exchange analysis system by Medical Graphics Corporation (St. Paul, Minn.).
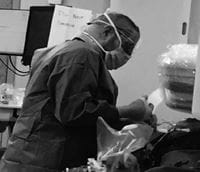
Figure 2: Dr. Michael Risbano performing a right heart catheterization.
Shortly after, the patient is placed on the stationary bicycle in the cardiac cath lab where the stages of freewheel (no resistance applied) and four to five stages of ramped exercise are performed. The ramp chosen depends upon the patient’s demographics and level of personal fitness. Hemodynamics and blood work are obtained every two minutes during exercise. Simultaneous blood gas measurements taken from the pulmonary artery and radial artery catheter allow for measurement of direct Fick cardiac output as well as oxygen saturations and lactate levels. We routinely calculate oxygen content from the pulmonary artery and radial artery to assess for peripheral oxygen extraction. Patients exercise until limited by symptoms of fatigue, leg fatigue, dyspnea, chest pain, or a combination of these symptoms. If a patient is not limited by symptoms, the study is completed after eight to 12 minutes of exercise, preferably a peak exercise study. Finally, a cool down is done and recovery hemodynamics are measured.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension is defined as a resting mean PA pressure (mPAP) >25 mmHg and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) >3.0 Wood units (WU). Normal resting hemodynamics are mPAP <25 mmHg and PVR <3.0 WU. We define exercise pulmonary arterial hypertension while upright as mPAPpeak >30 mmHg, total pulmonary resistance (TPRpeak) >3.0 WU with a pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP) peak <20 mmHg. If the PAWPpeak is >20 mmHg, this constitutes an abnormal pulmonary venous response to exercise and may indicate heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (EF) in patients with a normal EF percentage and no valvular disease.
Patients referred for ACPET will include those with complaints of dyspnea on exertion or exercise fatigue that has not been fully explained by previous studies, or the causative disease state is unclear. The majority of patients referred to the ACPET Program will have been seen by either a primary care physician or a subspecialty physician, such as a pulmonologist, cardiologist, rheumatologist, or geriatrician.
Patients referred for testing may include those with dyspnea and histories of connective tissue disease (scleroderma in particular), diastolic dysfunction (heart failure with preserved ejection fraction), pre-pulmonary or pre-cardiac transplant, valvular heart disease, post-pulmonary embolism, parenchymal lung disease (interstitial lung disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis), peripheral myopathy, and various forms of pulmonary hypertension, including pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Initial routine testing is required prior to performing ACPET including echocardiogram, pulmonary function testing, and chest imaging. As previously mentioned, for some patients these tests may be unrevealing or may demonstrate multiple abnormalities such as concomitant lung disease and pulmonary hypertension or diastolic dysfunction. This technique provides a comprehensive ACPET to study and diagnose all forms of abnormal cardiopulmonary vascular and musculoskeletal responses to exercise for clinical and research purposes.
In a single-center study that performed a high volume of ACPETs, the authors demonstrated that the workup of exertional dyspnea in a multidisciplinary setting including ACPET dramatically reduced the time to diagnosis compared to routine testing alone.5 Typical diagnoses made with the study include exercise pulmonary arterial hypertension, exercise pulmonary venous hypertension, ventilatory limitation, oxidative myopathy, and dysautonomia/preload insufficiency.6
Commercial insurance typically covers the ACPET study.
For any patients who have continued dyspnea despite comprehensive testing and interventions, referrals can be made by calling 1-877-PH4-UPMC or emailing PHprogram@upmc.edu.
Referrals can also be made to Dr. Risbano directly at risbanomg@upmc.edu.
For more information about the ACPET Program, including patient information and frequently asked questions, please visit our website at www.upmc.com/acpet.